What is Binary
What is “binary”?
Binary means two states or conditions. There’s no third candidate so the state must be either the first one or the second one. For example:
- a light is on/off
- a door is close/open
- you have finished/not finished your assignment
- today is/is not New Year.
All of them represent 2 opposite conditions in a certain situation. In the area of computer and machine, we use 0 and 1 to represent those two states.
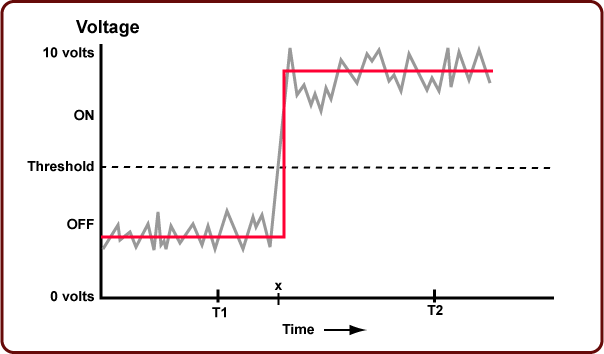
Take microprocessor for example, it can generate either high (1) or low(0) voltage.
Even there is some noise or bias when maintaining that voltage, the boundary between two states is so clear, that machine can distinguish them without making mistakes.
Why using “binary”?
Thus, we can summarise the advantages of applying binary digits:
- easy to build
- if there are three or more than three states, it is hard to identically distribute each state an accurate weight.
- For example, if three states are possible, that means you need to give each a weight of 33.33%
- immune noise or disruption
- two states are too different to mix them, although a relatively large noise exists.
- The info in binary format will remain clearly. You can also restore and then create a perfect copy of binary signals.
- can represent natural states
- most situations have two sides, that means you can represent them easily in binary format, and implement those into real machine execution
Reference
All articles on this blog are licensed under CC BY-NC-SA 4.0 unless otherwise stated.
Comments